SQL LAG() Function in SQL Server 2012 for Calculating Previous Value
SQL LAG() function is one of the recent enhancements among SQL Analytic Functions introduced with Denali, CTP3 for SQL Server 2012 developers. What SQL Server Lag() function does is returning simply the previous-next Nth row value in an order. The order of the rows can be grouped by using the Partition By clause for powering the SQL Lag() function.
Here is the SQL Analytic LAG() function syntax for T-SQL developers
LAG (scalar_expression [, offset], [default]) OVER ([partition_by_clause] order_by_clause)
The Lag() function input offset argument determines the number of previous rows in order that the SQL Engine will read from. Offset input parameter is optional. If nothing is provided, then the default value 1 will be used in LAG() function
The default argument sets the value which will be returned if SQL Lag() function returns nothing.
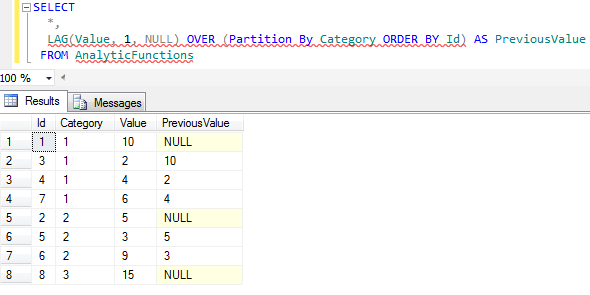
Here is our first SQL Server Lag() function example. If you look at the returned result set of the below SQL query, you will realize that all data from AnalyticFunctions table is listed. Besides the value of the previous row when ordered by Id column with the same Category value is displayed in PreviousValue column.
You see, the Lag() function offset argument is 1 as default value. This returns the previous row value. And the Lag() function default argument is NULL. Since the first row for each category does not have a previous row, the SQL LAG() function cannot calculate the PreviousValue column, and returns the default NULL value.
SELECT
*,
LAG(Value, 1, NULL) OVER (Partition By Category ORDER BY Id) AS PreviousValue
FROM AnalyticFunctions