Display Data in Multiple Columns using SQL
SQL developers can display different data rows from a database table on multiple columns of a single line. You can imagine the output layout like multiple column page layout in MS Word, for example.


Displaying data in multiple columns is not a difficult task if you know how to approach the problem. This SQL tutorial will share a method using SQL Row_Number() function and SQL CASE conditional statements in order to fulfill this task.
If you run a SELECT statement on an entity table on any database, the result will be something like below. All data will be listed under a single column. But if the app developers want to display data not in a single column format, but more than one column.

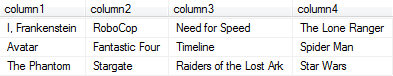
Assume that the web developer wants to display a movie list in 3 or 4-columns.
Then how should the database developers provide data to the user interface layer?
What should be the SQL code like that will be used to SELECT data in the desired format in SQL Server?
This Transact-SQL tutorial will be trying to answer all these questions and provide a solution method for SQL programmers for such requirements.
Let's start out SQL tutorial by defining our sample database table Movie which will store a list of movies.
As a developer, our technical requirement is to provide most recent 100 movie titles as list formed of four columns of movie titles.
Actually this is like a database table which has 4 movie title columns.
For the sake of simplicity and less INSERT statements below, instead of 100 movie titles, I'll only list top 12 entities. So I only provide 12 INSERT INTO statements to populate database table movie with sample data.
create table movie (
id int identity(1,1),
title nvarchar(200),
year int,
genre varchar(40)
)
insert into movie select ('Star Wars'), 1977, 'Fantasy'
insert into movie select ('Spider Man'), 2002, 'Fantasy'
insert into movie select ('Stargate'), 1994, 'Sci-Fi'
insert into movie select ('Avatar'), 2009, 'Fantasy'
insert into movie select ('Timeline'), 2003, 'Sci-Fi'
insert into movie select ('Fantastic Four'), 2005, 'Fantasy'
insert into movie select ('The Phantom'), 1996, 'Action'
insert into movie select ('I, Frankenstein'), 2014, 'Fantasy'
insert into movie select ('The Lone Ranger'), 2013, 'Action'
insert into movie select ('Raiders of the Lost Ark'), 1982, 'Action'
insert into movie select ('RoboCop '), 2014, 'Action'
insert into movie select ('Need for Speed'), 2014, 'Action'
As I said before, if you have thousands of data and you are dealing only with a hundred of them, you can set the WHERE clause in below SQL SELECT as "RowNumber <= 100"
Such a change in WHERE clause will enable SQL developers to list only 100 entities (or in our case movie titles).
with cte as (
select
*,
rownumber = ROW_NUMBER() over (order by year desc)
from movie
)
select
*,
((rownumber-1) / 4) + 1 as linenumber,
((rownumber-1) % 4)+1 as colnumber
from cte
where rownumber <= 12 -- this criteria can be updated for 100 rows
Since above SQL SELECT returns 12 rows on 4 columns, at the end of the process there will be only 3 lines each containing 4 movie titles.
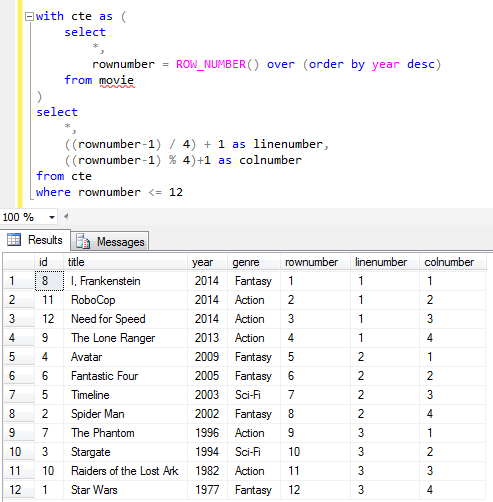
SQL Row_Number() function used with Mod and Integer Division enables display data in columns and rows format
The next step after above raw data is created is to map titles in rows with line number 1 to first row of the next dataset, and rows with line number 2 to second row, etc.
While mapping entities to their new rows, we should be coding our SQL script so that the movie with colnumber 1 is under the first column, movie with colnumber 2 is under the second column, etc.
I'll now wrap the above SELECT statement with a new SQL CTE structure. I prefer to use a SQL CTE (Common Table Expression) instead of a sub-select statement because you can refer to CTEs more than once like a temp table. And using the title, row number and column number fields I'll create an additional SELECT statement in multiple-CTE form.
Here is the SQL codes which is one step improved on the above Select statement.
with cte as (
select
title,
rownumber = ROW_NUMBER() over (order by year desc)
from movie
), dataset as (
select
title,
((rownumber-1) / 4) + 1 as linenumber,
((rownumber-1) % 4)+1 as colnumber
from cte
where rownumber <= 12
)
select
linenumber,
case colnumber when 1 then title else NULL end as column1,
case colnumber when 2 then title else NULL end as column2,
case colnumber when 3 then title else NULL end as column3,
case colnumber when 4 then title else NULL end as column4
from dataset
As you can see the screenshot of the resultset of above SQL script, the mapping of title column of each table row is mapped to correct columns successfully.
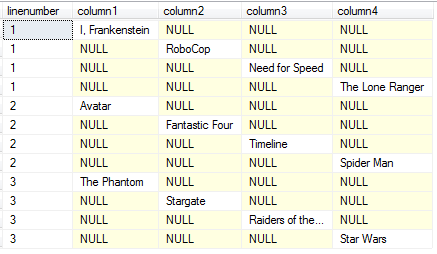
SQL CASE statement on "column number" field will help SQL developers to display each row data as a column field
Now SQL GROUP BY statement for an aggregation on LineNumber column will aggregate 4 lines with sample linenumber into a single line resulting with the desired output for 4 column display.
with cte as (
select
title,
rownumber = ROW_NUMBER() over (order by year desc)
from movie
), dataset as (
select
title,
((rownumber-1) / 4) + 1 as linenumber,
((rownumber-1) % 4)+1 as colnumber
from cte
where rownumber <= 12
)
select
linenumber,
max(column1) as column1,
max(column2) as column2,
max(column3) as column3,
max(column4) as column4
from (
select
linenumber,
case colnumber when 1 then title else NULL end as column1,
case colnumber when 2 then title else NULL end as column2,
case colnumber when 3 then title else NULL end as column3,
case colnumber when 4 then title else NULL end as column4
from dataset
) list
group by linenumber
And finally our SQL SELECT statement produces the below desired output. SQL script listed given number of rows on different columns of a new result set. User interface programmers can now easily display below data on a gridview or data grid for a multi-column reporting.
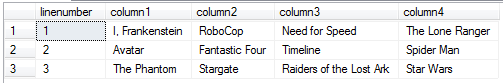
Here is the data rows listed in four columns using SQL programming
