List of SQL Servers using sqlcmd Utility
sqlcmd Utility enables database administrators to list servers where SQL Server is installed in local network. List of SQL Servers in your network can be prepared by using running sqlcmd utility sqlcmd.exe with -Lc option easily. If you carefully check the SQL Server sqlcmd utility options, you will see the -L option and its "c" optional parameter. The -L sqlcmd command option provides the easiest way for SQL Server database administrators to lists names of the locally configured server computers broadcasting on the network.
It is a common requirement for many SQL Server database administrators to find out any unknown SQL Server database server installations in their responsibility areas. For reports and to list installed SQL Server computers, the easiest method is to use SQLCMD Utility provided by Microsoft which comes default with SQL Server installation.
If SQLCMD utility is used with -L option, it generates a list of locally configured server computers. In the SQL Server list the names of the servers broadcasting on the network are listed. SQLCMD can list servers up to 3000 SQL Server names in the execution result.
If "c" (clean output) optional paramater is used with -L (list servers) option, only the SQL Server names will be returned in the result dataset of SQLCMD utility execution. Unnecessary text and informative descriptions will be omitted therefore the result set is called as clean output of list of SQL Servers in the network.
For more syntax options and sqlcmd parameters that SQL developers or database administrators to use with sqlcmd commands, please read the SQL reference for sqlcmd at MSDN.
SQL Server List
A SQL Server database administrator or a database developer can open the CMD promt and following sqlcmd command in the command promt to list SQL Server computers in the network.
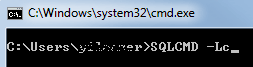
SQLCMD -Lc
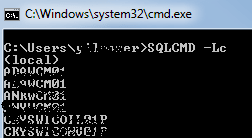
And the returned list of SQL Server installed servers will be as similar in the following screenshot. Since c clear output option is stated beside -L list option in sqlCmd utility, only the SQL Server names are listed without any additional information.
Of course, it is also possible to run SQLCmd utility command from SQL Server Management Studio query editor window. The only restriction may be the use of xp_cmdshell. If xp_cmdshell use is enabled on the SQL Server instance, admins or developers can execute following SQL command at query editor window.
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'sqlcmd -Lc'
The execution of the above xp_cmdshell SQL statement will return the same SQL Server list running locally in the network.
Using SQLCmd and xp_cmdshell utility tools in SQL Server, I code following SQL stored procedure which will store installed SQL Server computer names in the network and list SQL Server database servers as a result set. If you are using SQL Server 2005, you can use following SQL procedure too.
CREATE PROC sp_ListSQLServersInNetwork
AS
IF OBJECT_ID('SQLServerListInNetwork', 'table') is null
CREATE TABLE SQLServerListInNetwork (
id int identity(1,1),
servername nvarchar(100)
)
TRUNCATE TABLE SQLServerListInNetwork
INSERT INTO SQLServerListInNetwork (servername) EXEC xp_cmdshell 'sqlcmd -Lc'
DELETE FROM SQLServerListInNetwork WHERE servername IS NULL
SELECT * FROM SQLServerListInNetwork
GO
EXEC sp_ListSQLServersInNetwork
But if you have a SQL Server 2008 or a successor version of SQL Server 2008 where SQL Merge command can be used, I can suggest the below stored procedure. You can use this stored procedure to list SQL Servers on your network and run periodically by using a SQL job to trace new installations and uninstallations.
CREATE PROC sp_ListSQLServersInNetwork
AS
IF OBJECT_ID('SQLServerListInNetwork', 'table') is null
CREATE TABLE SQLServerListInNetwork (
servername nvarchar(100),
firstactivity datetime,
lastactivity datetime
)
DECLARE @serverlist AS TABLE (servername sysname null, activitydate datetime default getdate())
INSERT INTO @serverlist(servername) EXEC xp_cmdshell 'sqlcmd -Lc'
DELETE FROM @serverlist WHERE servername IS NULL
MERGE SQLServerListInNetwork
USING
(
SELECT servername, activitydate firstactivity, activitydate lastactivity
FROM @serverlist
) NewData ON SQLServerListInNetwork.servername = NewData.servername
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET SQLServerListInNetwork.lastactivity = NewData.lastactivity,
SQLServerListInNetwork.firstactivity = ISNULL(SQLServerListInNetwork.firstactivity, NewData.lastactivity)
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET THEN
INSERT VALUES(servername, firstactivity, lastactivity);
SELECT * FROM SQLServerListInNetwork
GO
EXEC sp_ListSQLServersInNetwork
As a result, all above methods for obtaining a SQL Server list on your network use the SQLCMD utility sqlcmd.exe -Lc option. But for a database administrator to have a report of SQL Servers list is very valuable. I hope we can find a way to extend the above stored procedures to list all SQL Server instances on the current network.
