Check HANA Database Table Size using HANA Studio
SAP HANA database administrator or SQLScript developers can use SAP HANA Studio to check database table sizes on disk to see how much disk space each SAP table uses. Disk space used by each SAP table can be viewed by using HANA Studio Administration cockpit visually or using SQL Console by querying M_TABLE_PERSISTENCE_STATISTICS monitoring table.
Using SAP HANA Development perspective, using Systems tab find your SAP HANA database system from the list.
![]()
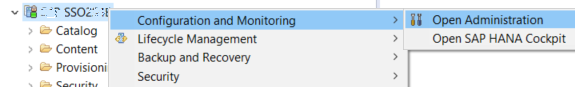
Right click on the target SAP HANA database using System window in SAP HANA Studio
Using the context menu, follow options Configuration and Monitoring > Open Administration
Administration cockpit will provide SAP HANA Studio users a huge amount of data about the HANA database that the SAP system is running on.
Switch to System Information tab.
A list tools or HANA database applications will be listed as in below screenshot.
SAP HANA Studio users can use the Size of Tables on Disk tool which enables developers to see the size of HANA database tables on disk in bytes.
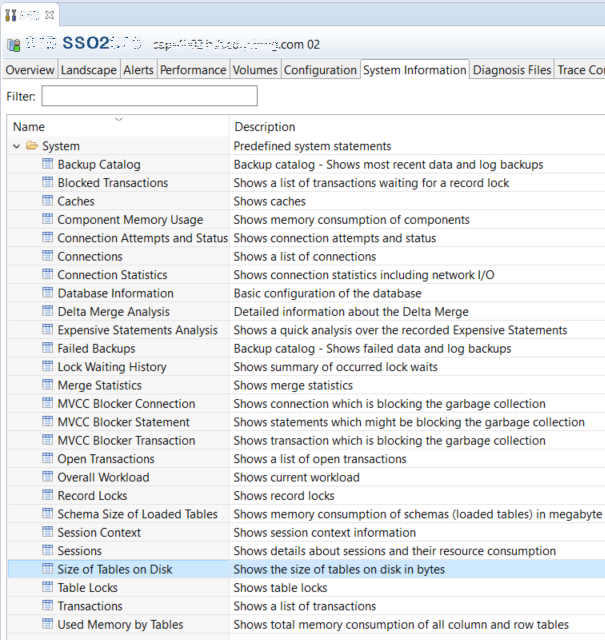
Double click on the Size of Tables on Disk tool for default use.
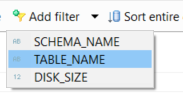
Using Add filter button, SAP HANA Studio users can addd filters like table disk size, table name or schema name to minimize the list of tables you are dealing with on the return list.
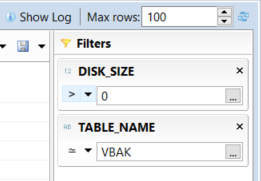
When you run the query to list the SAP HANA database tables and their disk sizes, a result set similar to below will be displayed. Please note that the size column value is in bytes.
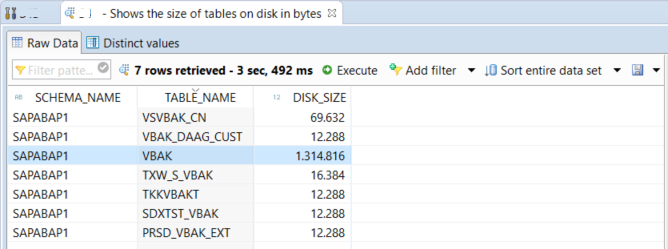
Of course, if you are an experienced SQL programmer it is an option to type your query for additional information on the System Information tool.
On the Administration cockpit, instead of double click on the "Size of Tables on Disk" or Execute the tool immediately, right click on from context menu choose
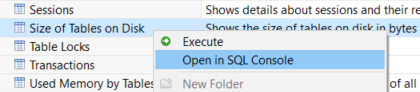
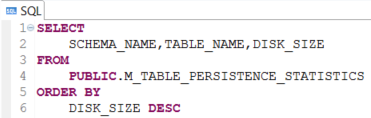
Here is the default SQLScript query for displaying SAP HANA database table sizes on disks
Of course, SQL developer can use other fields from M_TABLE_PERSISTENCE_STATISTICS like page_count, read_count, write_count, bytes_read, etc. by modifying your SQL query
SELECT
SCHEMA_NAME,TABLE_NAME,DISK_SIZE
FROM
PUBLIC.M_TABLE_PERSISTENCE_STATISTICS
ORDER BY
DISK_SIZE DESC