Create AMDP Procedure using SAP HANA Studio with ABAP
This SAP HANA AMDP tutorial is for ABAP programmers who are new to create AMDP procedures using SAP HANA Studio in ABAP. I want to share a basic AMDP procedure or AMDP class template that ABAP developers can copy and paste to start with a new AMDP class and AMDP method development including exception handling for SQLScript that will be executed on HANA database.
AMDP procedures are created using SAP HANA Studio as IDE (Integrated Development Environment). Although basically an ABAP class is created and a class method is used for each AMDP procedures that are created and executed on SAP HANA database, ABAP programmers have to follow some rules. In this document I want to share a very basic template that will help ABAP programmers who want to create an AMDP procedure.
Before we continue with AMDP creation steps on SAP HANA Studio, let's at least test our memory for what does AMDP stand for?
AMDP stands for ABAP Managed Database Procedure. Simply an ABAP programmer can create a HANA database procedure (SQLScript code block accepting parameters) without directly interfering with SAP HANA database.
So similar to ABAP IDE environments that the developer is used to, a database procedure can be created.
This procedure has an ABAP Data Dictionary entry as a DDIC object and can be transported using TMS transport requests.
Let's start from the beginning. First of all, launch SAP HANA Studio. Developers will be using SAP HANA Studio for AMDP class developments.
ABAP programmers cannot create AMDP classes using SAP GUI. The only development environment for ABAP developers to create AMDP procedures and AMDP class methods is SAP HANA Studio.
On the target ABAP development package, right click on package name and on context menu follow menu options: New > ABAP Class
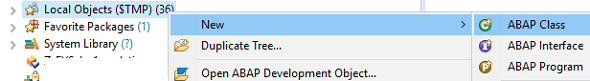
Provide class name and description. Then click on Next to assign a transport request for the development. If you are building these objects as local objects then press Finish button.
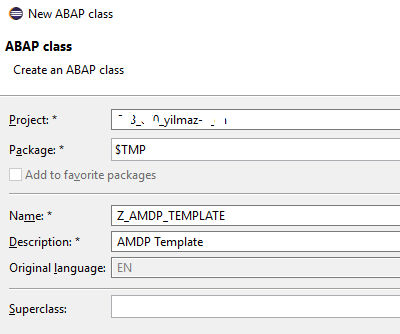
This is the default ABAP code for your new class.
This class is not an AMDP class yet. It is still an ordinary ABAP class definition.
CLASS z_amdp_template DEFINITION
PUBLIC
FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS z_amdp_template IMPLEMENTATION.
ENDCLASS.
The trick to convert an ABAP class into an AMDP procedure class is implementing the if_amdp_marker_hdb interface as follows
CLASS z_amdp_template DEFINITION
PUBLIC
FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_amdp_marker_hdb.
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS z_amdp_template IMPLEMENTATION.
ENDCLASS.
Let's now create our first AMDP method.
Define importing and exporting parameters of the AMDP procedure.
class-methods get_company_name
importing value(company_code) type bukrs
exporting value(company_name) type butxt
raising cx_amdp_error.
A red mark will appear on the left side of the code editor indicating that the implementation is missing for this new AMDP method.
Click on the red mark and from possible actions suggested, click on add implementation for the new method.
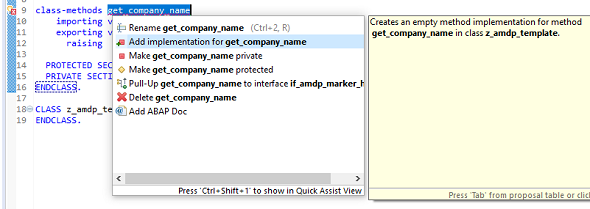
Resultant ABAP code will be as follows
CLASS z_amdp_template DEFINITION
PUBLIC
FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_amdp_marker_hdb.
class-methods get_company_name
importing value(company_code) type bukrs
exporting value(company_name) type butxt
raising cx_amdp_error.
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS z_amdp_template IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD get_company_name.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
You can still activate and build the new class code without any issue.
Add following lines in your AMDP method implementation. Please note that the HANA database tables used are listed after "using" phrase
So it will be as follows:
METHOD get_company_name
by database procedure
for hdb language sqlscript
options read-only
using T001.
ENDMETHOD.
Now you have the following error: The body of a database procedure cannot be empty. and prevents activating your AMDP class.
Because AMDP procedure requires SQLScript code to execute on HANA database
Add following SQLScript code in your method implementation.
select butxt into "COMPANY_NAME" from T001 where bukrs = :company_code;
This SAP HANA SQLScript Select statement reads butxt field into company_name parameter from T001 database table for the record that has bukrs field value is equal to company_code parameter value.
This SQL code can be implemented easily with OpenSQL as ABAP developers know. Actually SQLScript is very handy and provides performance for more complex SELECT statements.
Please note that parameters or variables is used differently in this SQLScript statement.
If you refer to its value as here in WHERE clause for the company_code, database developers should add ":" in front of the parameter name.
If you are assigning a value to the parameter, you don't need an identifier.
Although I have just said there is no need, in a SELECT statement if you assign a value, identify the target parameter between ' " ' and use capital letters.
Our first AMDP procedure code is now as follows.
Please note that we have added raising cx_amdp_error for exception throwing whenever a problem occurs in our SAP HANA AMDP procedure code.
This will be very useful for troubleshooting when we consume this AMDP procedure from our ABAP programs.
CLASS z_amdp_template DEFINITION
PUBLIC
FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_amdp_marker_hdb.
class-methods get_company_name
importing value(company_code) type bukrs
exporting value(company_name) type butxt
raising cx_amdp_error.
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS z_amdp_template IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD get_company_name
by database procedure
for hdb language sqlscript
options read-only
using T001.
--> SQLScript
select butxt into "COMPANY_NAME" from T001 where bukrs = :company_code;
--< SQLScript
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
ABAP programmers who are familiar with SQLScript will realize at first that the codes within the class method implementation are SQLScript.
For example for commenting code in ABAP ( " ) can be used or at the beginning of the related line ( * ) is used.
But in this AMDP method codes, to comment code we have used ( -- )
So ABAP programmers can place their SQLScript codes between commented lines:
--> SQLScript and
--< SQLScript
Now activate your AMDP class code.
Then create a sample ABAP program that you can consume this HANA AMDP class methods.
ABAP developer can copy and paste following codes to call AMDP procedure within ABAP codes.
DATA lv_bukrs TYPE bukrs VALUE 'TR26'.
TRY.
CALL METHOD z_amdp_template=>get_company_name
EXPORTING
company_code = lv_bukrs
IMPORTING
company_name = DATA(lv_butxt).
CATCH cx_amdp_error INTO DATA(lv_exp).
WRITE lv_exp->get_text( ).
ENDTRY.
WRITE lv_butxt.
As seen in CATCH section of the TRY-CATCH block if any problem occurs in HANA database procedure, the AMDP class returns an exception where the ABAP programmer can get details of the error.
For example, if you pass a company code that does not exit in your SAP system, following exception text will be displayed from CATCH part.
no data found: "SAPABAP1"."Z_AMDP_TEMPLATE=>GET_COMPANY_NAME#stb2#20180809093640": line 9 col 3 (at pos 246): "SAPABAP1"."Z_AMDP_TEMPLATE=>GET_COMPANY_NAME": line 9 col 1 (at pos 254): no data found:
If the "raising cx_amdp_error" exception handling statement is not used in the AMDP method definition, while calling AMDP procedure method in ABAP you will experience ST22 code dumps.
So in order to implement a basic exception handling in AMDP procedures or for troubleshooting purposes against errors that can occur in SQLScript codes, this rasing cx_amdp_error definition is important.
